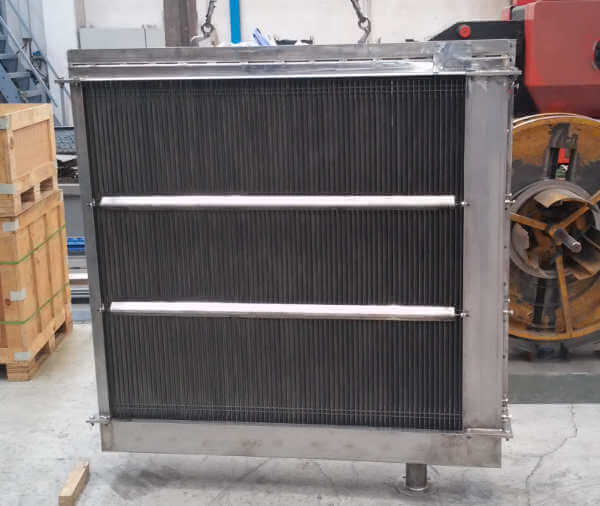
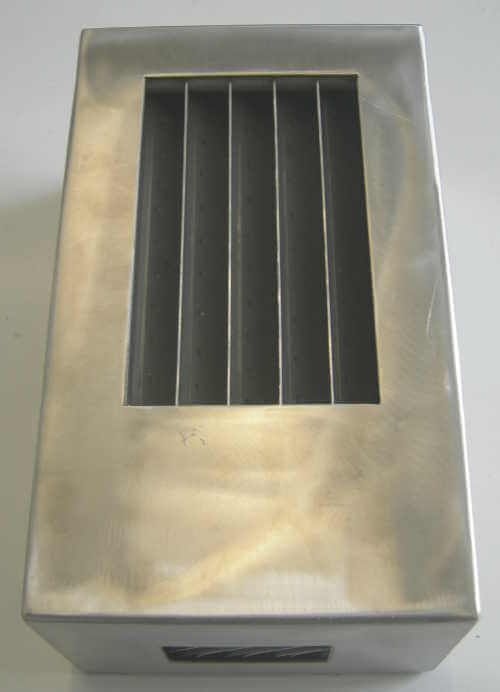
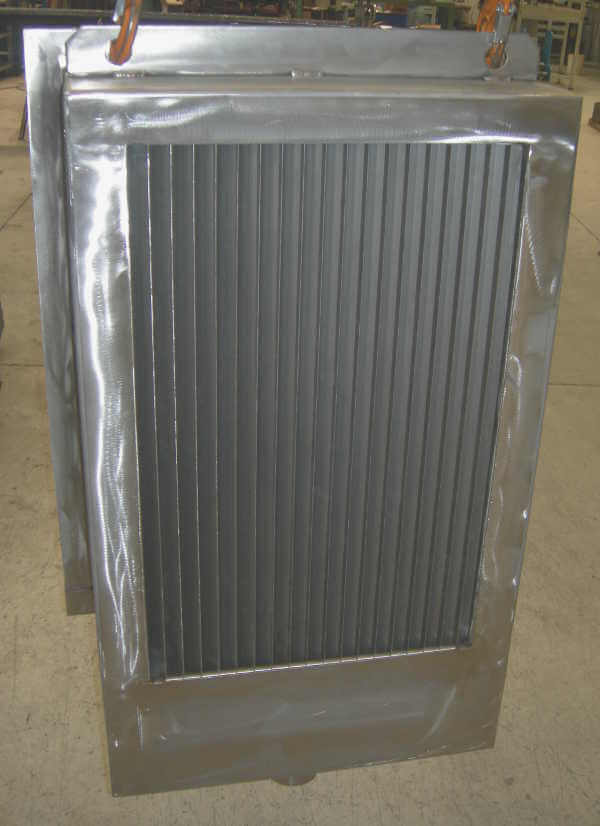
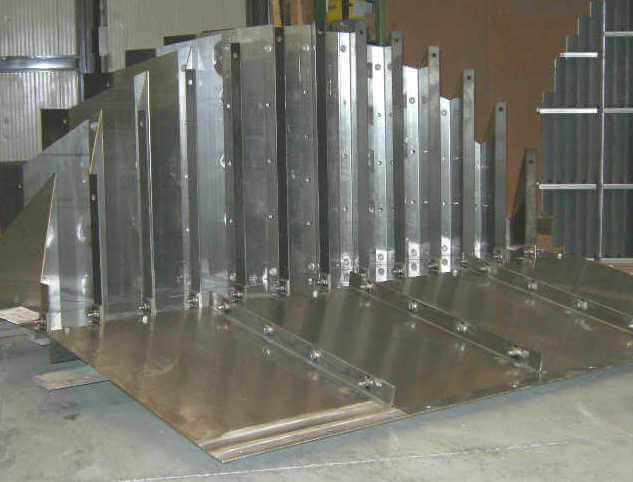
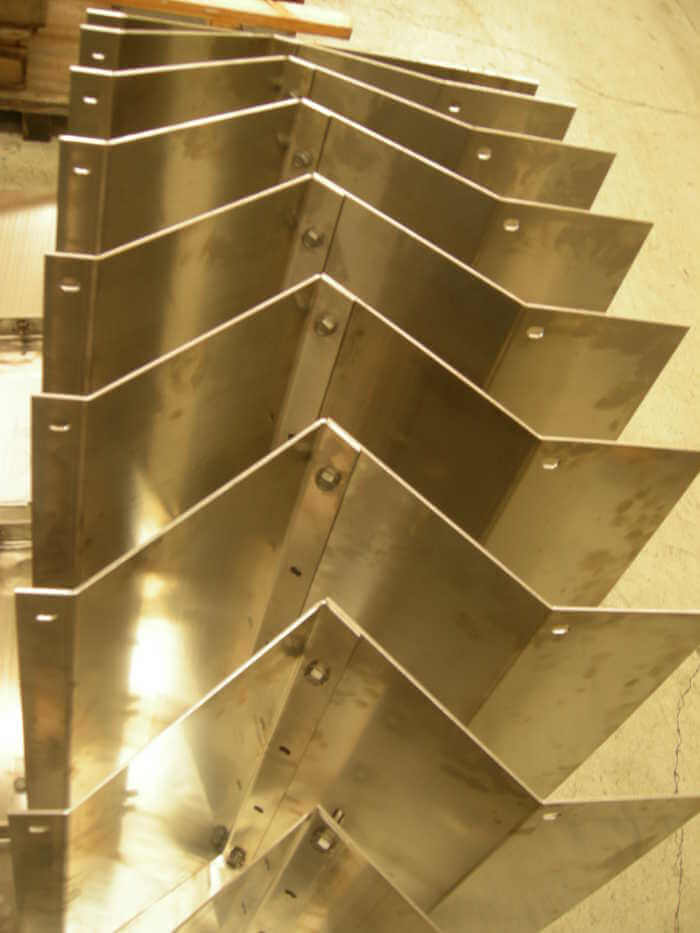
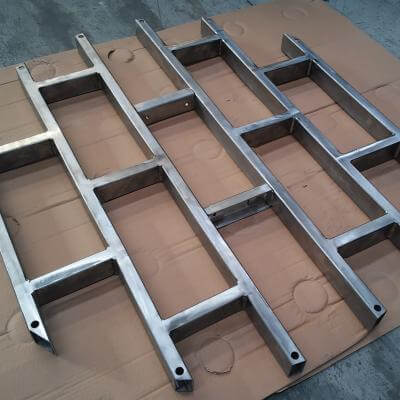
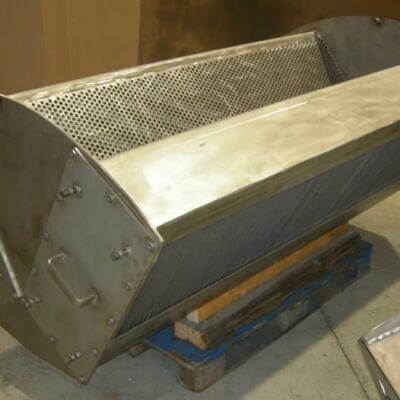
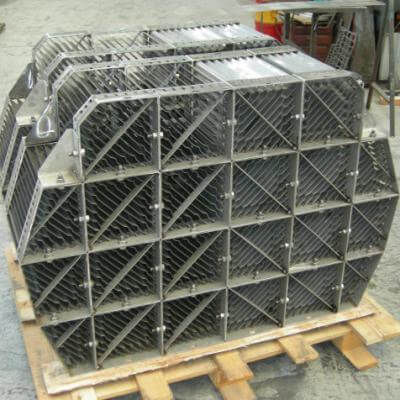
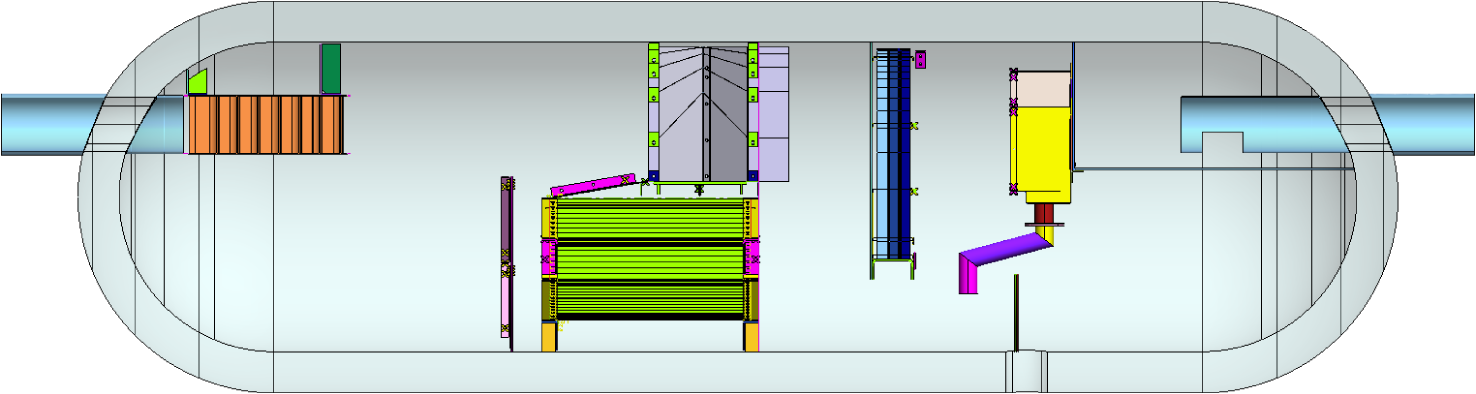
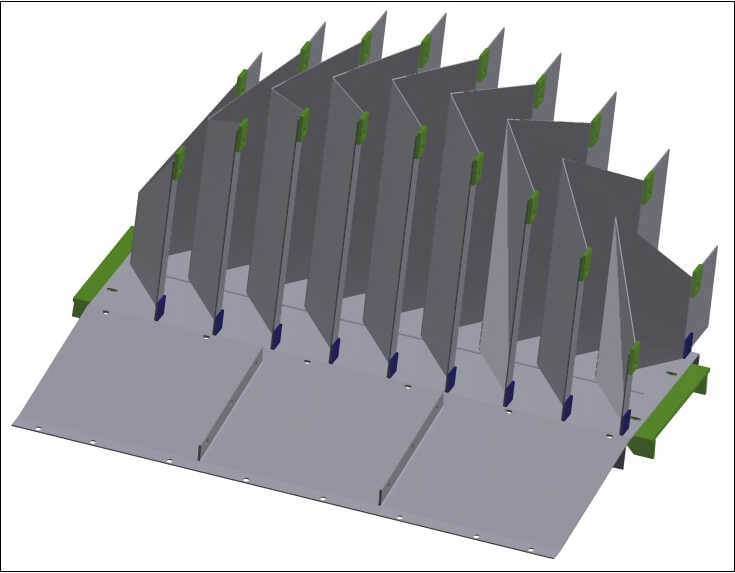
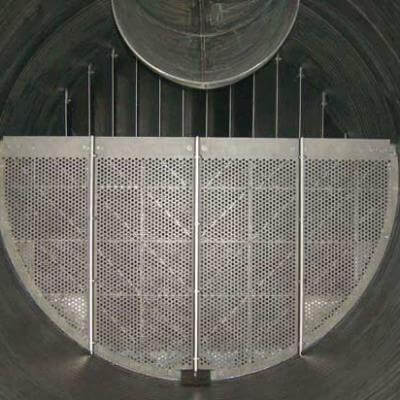
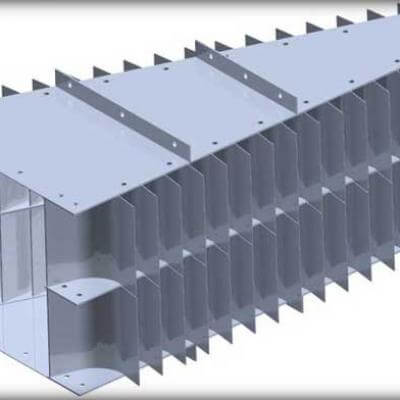
STANDARD VANE PACKS
Vane packs, with wire mesh separators, are the most widely used internals for the separation of liquid droplets carried by gaseous streams.
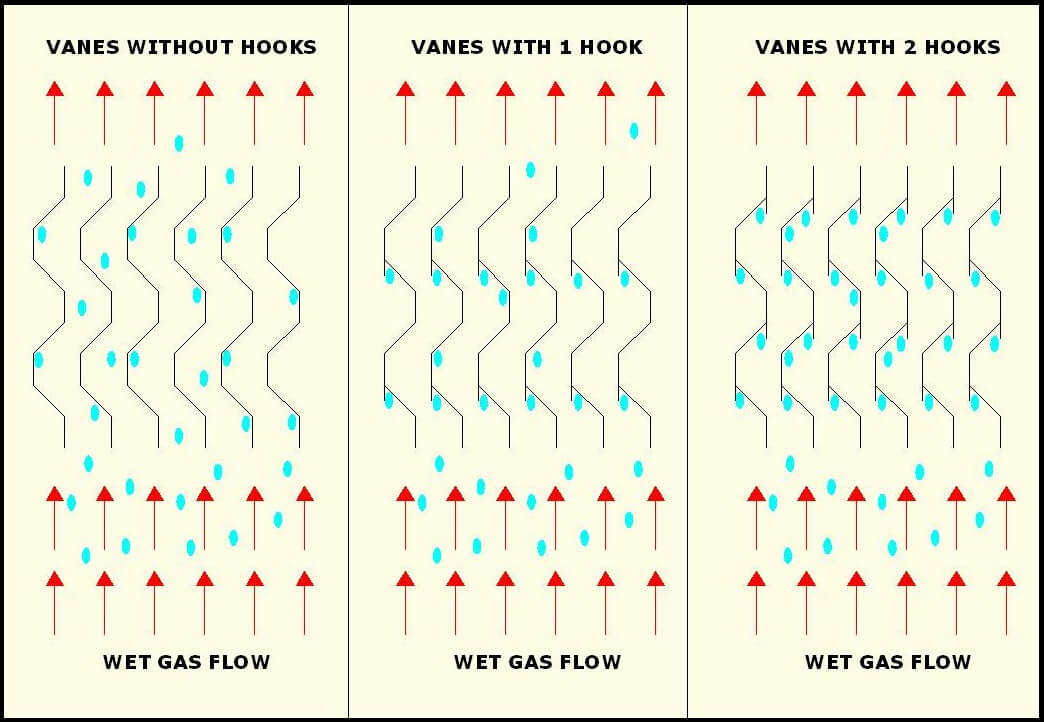
SEPARATION: vane packs are composed of sets of vane profiles where the gas passes through and, changing direction, clashes on the vanes being captured by the hooks. Liquid droplets slide down the vanes and are drained down by a tube into the liquid section of the vessel.
CROSSING SPEED: in comparison with wire mesh separators, the crossing speed is higher allowing a reduction of the crossing area, of the separator and of the vessel diameter.
PERFORMANCES: the diameter of the smallest separated liquid droplet is bigger than in a wire mesh separator. For this reason vane packs are not recommended when a high separation performance is required.
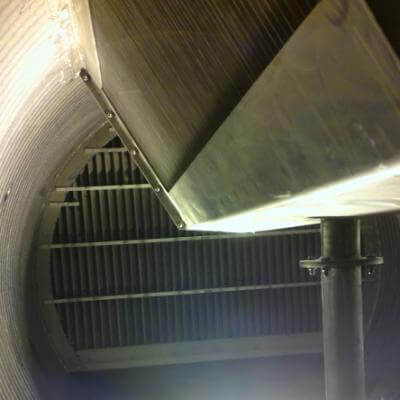
Center: explanation of droplets interception in different kinds of vane pack
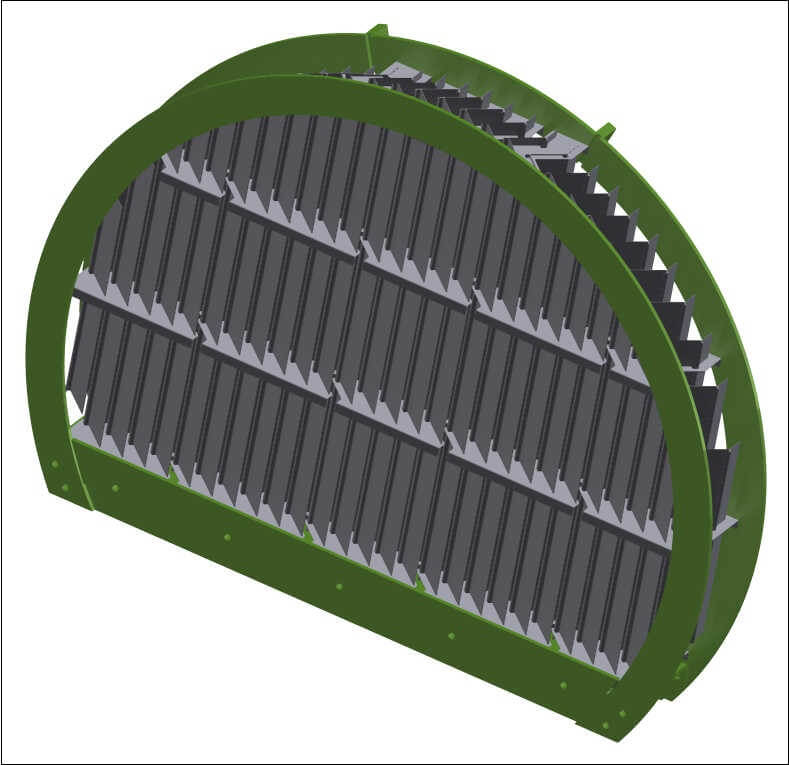
Right: a vane pack for vertical vessels
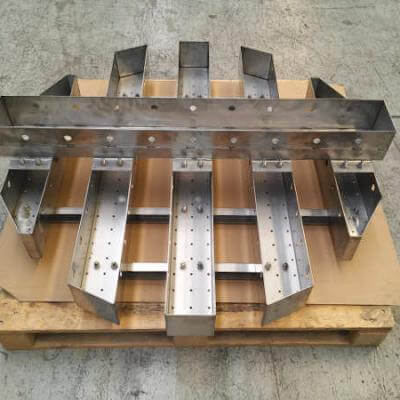
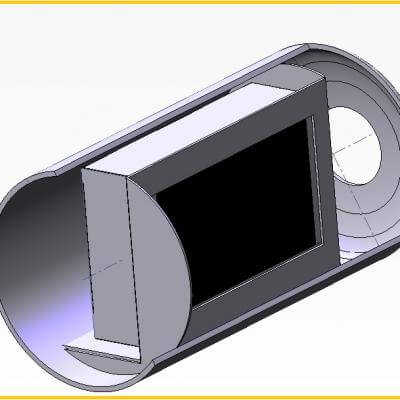
STRAIGHTNER
The straightener is a particular kind of vane pack used to break the foam and calm the gas flow. This internal is often placed between a rectifier and vane pack separator or a wire mesh demister.
GAS FLOW RECTIFIER
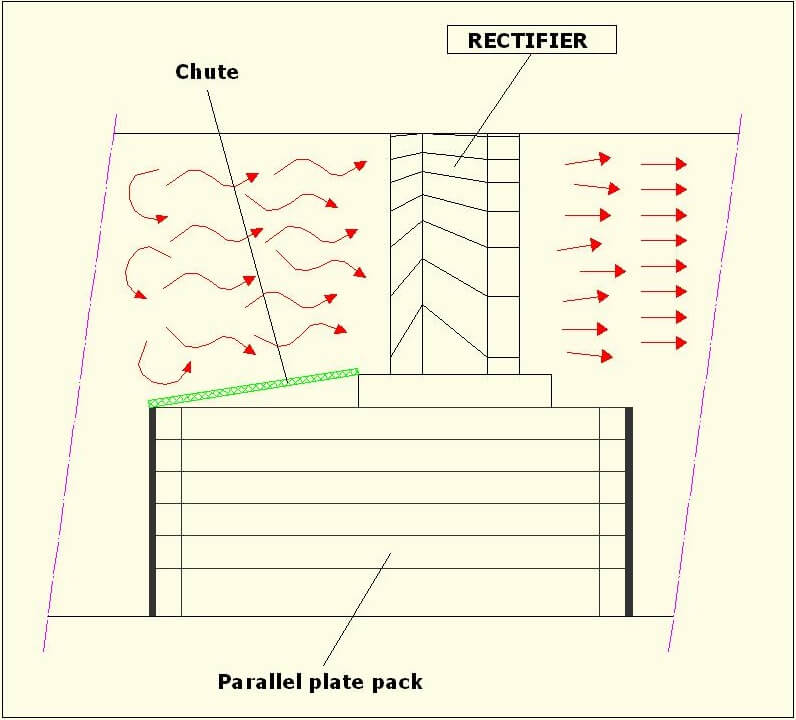
This special kind of vane pack is made with vanes forming large canals to rectify the chaotic gas flow from the inlet.
Passing through the flow rectifier, the gas is calmed and the flow rectified. This allows a proper distribution of the flow at the inlet of the next internals.
It's important to underline that the rectifier is not designed to separate liquid droplets from the gas flow but only to calm the flow.
These elements are usually located over the parallel plates pack to intercept and redirect the gas flow. Usually, a “chute” is placed before the rectifier to intercept the gas and feeding it in the rectifier.
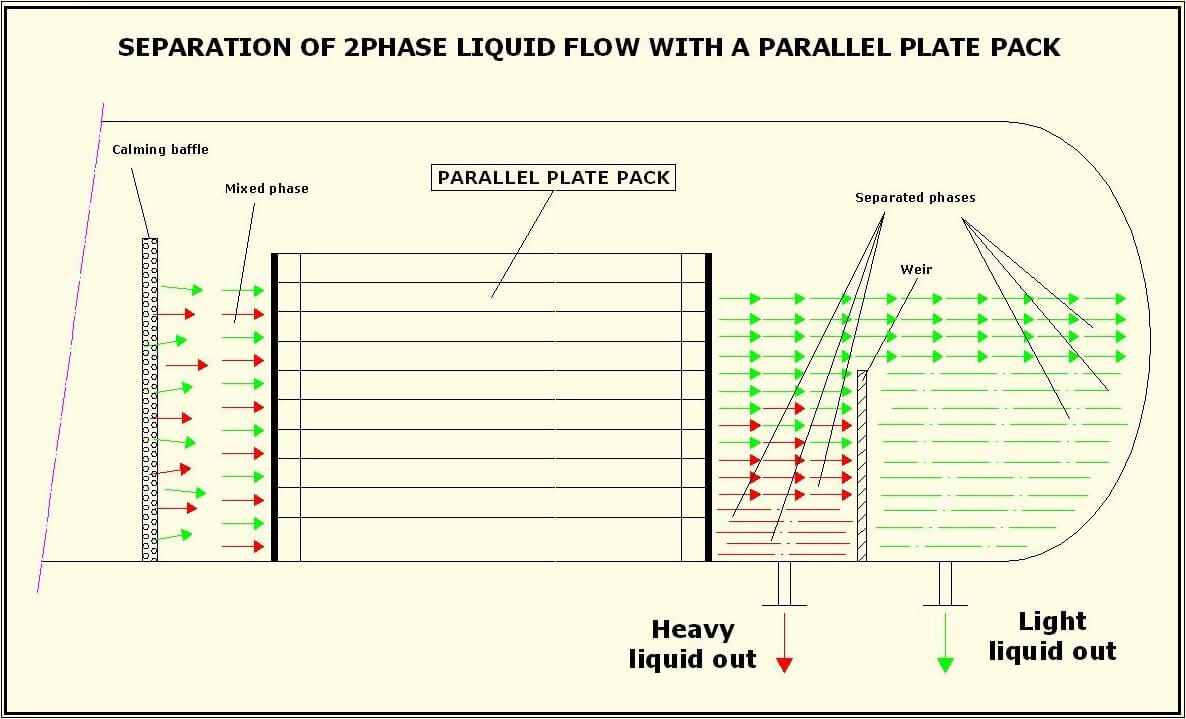
PARALLEL PLATE PACKS FOR LIQUID-LIQUID SEPARATION
This kind of internal is commonly implemented to separate a liquid-liquid mix using the different densities of the two liquids. They are often used in many three-phase separators where the flow is composed of gaseous phase, heavy liquid phase (ex. water) and light liquid phase (ex.: oil).
Read more: PARALLEL PLATE PACKS FOR LIQUID-LIQUID SEPARATION